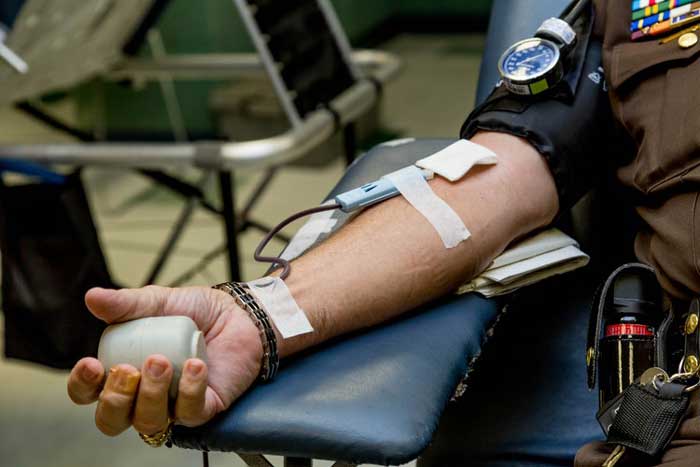
 Blood transfusion is a procedure that is used by modern medicine as the only alternative method of treating various diseases and saving lives after severe blood loss. During the war years, the wounded were saved this way. In modern medicine, heavy patients, such as cancer patients, who need to restore hemoglobin, red blood cells and platelets after undergoing chemotherapy, are rehabilitated due to blood transfusions. Let’s learn more about blood donation and the need for it.
Blood transfusion is a procedure that is used by modern medicine as the only alternative method of treating various diseases and saving lives after severe blood loss. During the war years, the wounded were saved this way. In modern medicine, heavy patients, such as cancer patients, who need to restore hemoglobin, red blood cells and platelets after undergoing chemotherapy, are rehabilitated due to blood transfusions. Let’s learn more about blood donation and the need for it.
How the process of blood donation is organized
Today, individual blood components are needed most often. Donated blood is then divided into elements and poured into the recipient (who needs a blood transfusion).
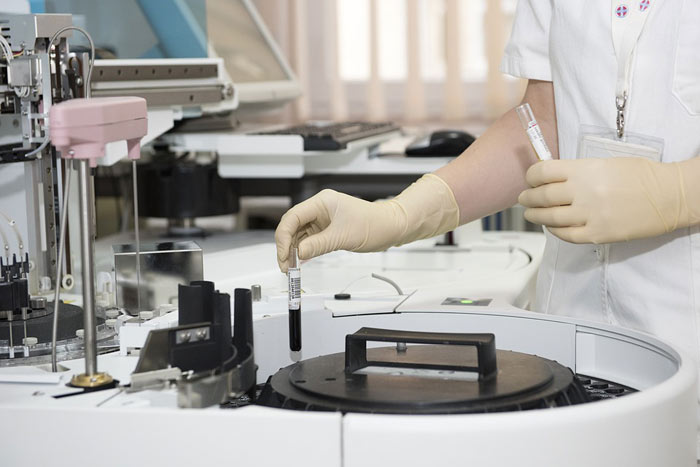
Blood transfusion (blood donation) is preceded by screening for the identification of various pathologies. Before the blood delivery procedure, the blood type and Rh factor of a person are determined, as well as the presence of the Cell antigen, which determines how well the donated blood will be accepted by the body – whether there will be no bright immune reaction to it after mixing Cell positive and Cell negative erythrocytes. Then the blood is examined for safety.
Blood transfusion process can be compared with an ordinary blood test. Blood is taken from the donor’s vein in the morning. This is not accidental since morning is defined as the most suitable time when the body responds adequately to blood loss. The earlier the procedure is done, the easier it is experienced by the body. In the afternoon, donating blood is usually recommended only to healthy and experienced donors. Donating blood on an empty stomach is not recommended, but it is necessary to observe restrictions concerning food consumption and taking alcohol 48 hours before donation. It is necessary to refrain from salty, smoked, spicy and fried foods, sugary carbonated drinks, some vegetables, and fruits, as well as from berries and nuts. You should not plan the procedure after a physically difficult, intensive period, for example, after a night duty or just a sleepless night, just before exams, competitions, delivery of the project, etc.
The blood transfusion procedure takes no more than 10 minutes, during which a person donates about 0.5 liters of blood. Special rest after transfusion is not required. It is only necessary to limit physical exertion for half an hour after blood donation and to refrain from smoking.
If the body does not accept the donated blood
Theoretically, such situations can arise if donated positive Rh factor blood is transfused to a recipient with Rh-negative blood or when Cell positive and Cell negative RBC are mixed. In this case, the recipient may experience a life-threatening condition called hemolysis — this is when the body perceives donor blood as foreign and produces specific antibodies that contribute to the destruction of red blood cells of the transfused blood.
In practice, such cases are avoided. That is why the donor donates blood for research before transfusion.
How donated blood is stored
Blood and its components have a maximum shelf life. In whole liquid form, blood can be stored for a day at room temperature. Longer storage is possible at 5-6 °C. In that case, blood preservation is possible during up to 4-6 weeks, which is considered the deadline when the red blood cell count is optimal for subsequent transplantation. For long-term storage, donor blood is taken from a vein under sterile conditions and is poured into special containers containing drugs that prevent clotting and the formation of blood clots, as well as glucose and sucrose, which are good nutrients for red blood cells, and, accordingly, preserve their vitality longer.
Specialists of the blood service have developed other methods for storing blood elements. Blood can be frozen, pre-equipped with the substances that allow maintaining the activity of red blood cells for a long time. Plasma is stored in special plastic packages in refrigerators at the temperatures of –200°C under constant monitoring of the temperature conditions. This method of blood preservation allows not only to transfuse it when needed but also to successfully replenish the stocks of rare blood groups.
Blood safety
Donated blood goes through many stages of testing. First of all, donors are checked for the presence of viral and infectious diseases. Absolute contraindications to donating blood are drug addiction, alcoholism, the presence of such diseases as hepatitis B and C, syphilis, HIV, chronic skin eczema, psoriasis, transplantation, partial transplantation or removal of vital organs. In addition, each donated dose of blood is necessarily examined for the presence of antigens, antibodies, viruses, DNA, RNA, and infectious agents.
Who cannot be a donor
In addition to carriers of these diseases, donors cannot include pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, patients with heart disease, acute renal failure, tuberculosis, cancer patients, people with brain pathologies, blood diseases, severe allergic reactions, infectious or chronic diseases in the acute stage.
Temporary contraindications for donation are acute respiratory viral infections or the flu. After successful treatment of the flu, you have to wait for a month and only then agree to the blood transfusion procedure. It is also impossible to transfuse blood within a week after tooth extraction, within a year after tattooing, a piercing procedure or an acupuncture treatment, within 5 days after the end of menstruation and within six months after an abortion.
Totally healthy donors donate blood regularly, but men can donate blood no more than 5 times a year, women cannot donate it more than 4 times per year. If contraindications are absent, plasma and platelets can be donated once every 2 weeks, and whole blood once in 2 months.
Are donors healthy people?
From the point of view of cleansing the body, blood transfusion can be considered the optimal method for updating the blood flow. In medicine, it is often compared with plasmapheresis, a method of cleaning blood plasma from toxins and pathologically harmful substances to enhance the immune processes in the body. It is also one of the components of complex therapy during health improvement or recovery after a long illness.
Therefore, any donor helping people helps himself in some way.